Theories about the Beginning of The Universe
How and when did the universe begin? No other scientific question is more fundamental or provokes such a spirited debate among researchers. The best that scientists can do is work out the most foolproof theory, backed up by observations of the universe. So far many people have come up with theories to explain the beginning of the universe but no one has come up with an indisputable explanation of how the cosmos came to be.
✧ The Big Bang Theory :
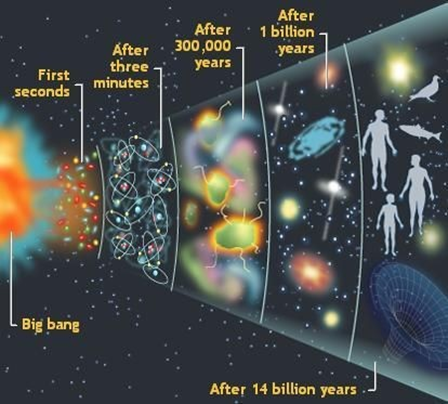
The Big Bang Theory is the leading explanation about how the universe began. At its simplest, it says the universe as we know it started with a small singularity (extremely small but incredibly dense point of mass/energy), then inflated over the next 13.8 billion years to the cosmos that we know today. In fact according to this theory matter and energy back then were the same thing and it was impossible to distinguish them from one another.
Supporters of Big Bang theory believe that this dense point of mass/energy exploded, and within seconds it ejected mass/energy at nearly the speed of light. Moments later mass and energy began to split apart and become separate entities as the universe started to cool down.
This theory came from an unusual finding in 1929, when astronomer Edwin Hubble working at Mount Wilson Observatory, California, announced that all the galaxies were receding from us and from each other at great speeds. He examined the light from distant galaxies using a spectroscope. He observed that light from galaxies far off in space was shifted to the red end. Hubble explained this red shift concluding that galaxies were in motion and moving away from Earth.
Big Bang theorists believe that the universe has been expanding since the Big Bang, and space itself is expanding no matter where you look.
Problem with the Big Bang Theory
One problem with this theory is that it predicts a smooth universe implying that the distribution of mass on large scale should be roughly the same.
But in 2001, astronomers announced the discovery of a group of galaxies and quasars which is presently the largest structure in the universe. Instead of an even distribution of matter, the universe seems to contain great empty spaces punctuated by densely packed streaks of matter.
Big Bang supporters maintain that their theory is not flawed. They argue that gravity from undetected objects in space attracts matter into clumps.
✧ The Steady State Theory :
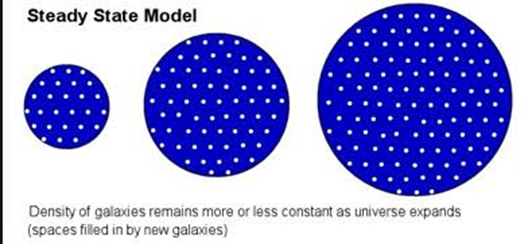
In the 1940s a hypothesis arose called steady space theory. British astrophysicists argued that the universe was not only uniform but also unchanging in time. Under this theory, the stars and galaxies may change but on the whole the universe always looked the way it is and it always will.
But as Big Bang theory predicted universe was receding creating empty spaces. Steady state theorists accepted that universe is expanding but predicted that new matter made up of hydrogen atoms continuously comes between these empty spaces. But how can something be created out of nothing?
°Problem with the Steady State Theory°
The idea of something created out of nothing violated the laws of physics that matter can neither be created nor be destroyed. But astronomers found it hard to directly disprove this because the amount of matter continuously created according to this theory was very tiny.
Steady State Theory still fails because if the matter is continuously created then the average age of stars in any part of the universe will be the same, but astronomers have found that this is not true.
✧ The Plasma Universe Theory :
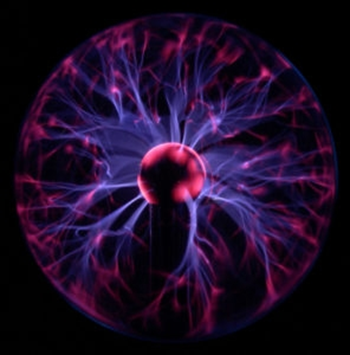
Another theory was given by Nobel laureate Hannes Alfven, a Swedish plasma physicist, called the Plasma Universe. He noted that 99% of the observable universe is made of plasma. This theory states that Big Bang never happened and the universe is crisscrossed by gigantic electric currents and huge electric fields. Under this view universe has existed forever under the influence of electromagnetic fields. Such a universe would have no beginning and no predictable end.
Little of the evidence for the Plasma Universe comes from direct observations of the sky. Instead, it comes from laboratory experiments. Computer simulations of plasmas subjected to high-energy fields reveal patterns that look like simulated galaxies. Using actual electromagnetic fields in the laboratory, researchers have also been able to replicate the plasma patterns seen in galaxies.
Problem with the Plasma Universe Theory
Proponents of plasma cosmology claim electrodynamics is as important as gravity in explaining the structure of the universe, and speculate that it provides an alternative explanation for the evolution of galaxies and the initial collapse of interstellar clouds. However, theoretical analysis shows that many scenarios for the generation of seed magnetic, which rely on the survival and sustainability of currents at early times i.e. Birkeland currents of the magnitude needed for galaxy formation do not exist. Also due to overall charge neutrality, plasma physics does not provide for very long-range interactions in astrophysics even while much of the matter in the universe is plasma.
Conclusion:
As with all the extraordinary claims, the key is verification by independent researchers, until confirmation is found it is important to be skeptical. Even with the evolution in technology with time, the theories attempting to solve this mystery keep getting complicated, the origin of the universe is still one of the biggest puzzles in cosmology.




